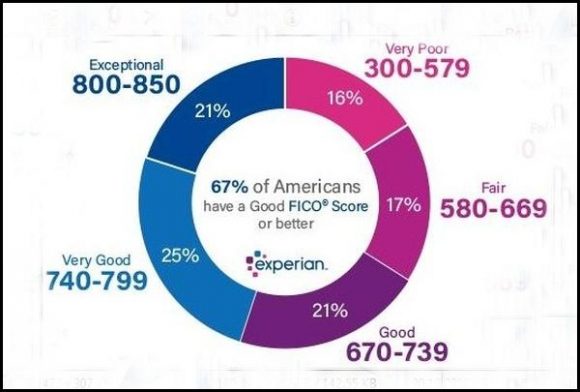
For a score with a range between 300-850, a credit score of 700 or above is generally considered good. A score of 800 or above on the same range is considered to be excellent. Most credit scores fall between 600 and 750. Higher scores represent better credit decisions and can make creditors more confident that you will repay your future debts as agreed.
Credit scores are used by lenders, including banks providing mortgage loans, credit card companies, and even car dealerships financing auto purchases, to make decisions about whether or not to offer your credit (such as a credit card or loan) and what the terms of the offer (such as the interest rate or down payment) will be. There are many different types of credit scores. FICO® Scores* and scores by VantageScore are two of the most common types of credit scores, but industry-specific scores also exist.
What Is a Good FICO® Score? One of the most well-known types of credit score are FICO® Scores, created by the Fair Isaac Corporation. FICO® Scores are used by many lenders, and often range from 300 to 850. Generally, a FICO® Score above 670 is considered a good credit score on these models, and a score above 800 is usually perceived to be exceptional.
Why credit scores mMatter
Credit scores are decision-making tools that lenders use to help them anticipate how likely you are to repay your loan on time. Credit scores are also sometimes called risk scores because they help lenders assess the risk that you won’t be able to repay the debt as agreed.
Having good credit is important because it determines whether you’ll qualify for a loan. And, depending on the interest rate of the loan you qualify for, it could mean the difference between hundreds and even thousands of dollars in savings. A good credit score could also mean that you are able to rent the apartment you want, or even get cell phone service that you need.
Think of your credit scores like a report card that you might review at the end of a school term, but instead of letter grades, your activity ends up within a scoring range. However, unlike academic grades, credit scores aren’t stored as part of your credit history. Rather, your score is generated each time a lender requests it, according to the credit scoring model of their choice.
Every time you set a major financial goal, like becoming a homeowner or getting a new car, your credit is likely to be a part of that financing picture. Your credit scores will help lenders determine whether or not you qualify for a loan and how good the terms of the loan will be.
However, credit scores are usually not the only things lenders will look at when deciding to extend you credit or offer you a loan. Your credit report also contains details which could be taken into consideration, such as the total amount of debt you have, the types of credit in your report, the length of time you have had credit accounts and any derogatory marks you may have. Other than your credit report and credit scores, lenders may also consider your total expenses against your monthly income (known as your debt-to-income ratio), depending on the type of loan you’re seeking.
Views: 329